Research
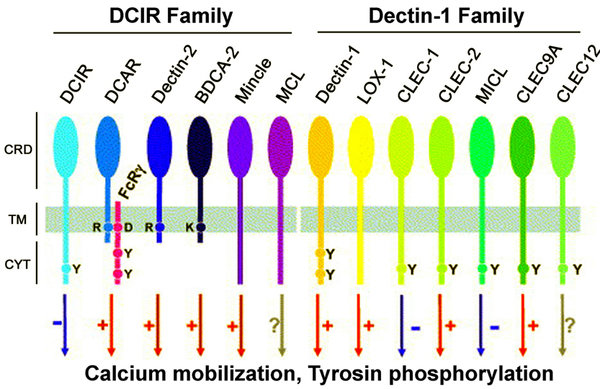
Our group focuses on the role of C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) in infection and inflammation. In our immune system, there are different classes of carbohydrate-binding receptors (so-called lectins) that recognize specific glycan structures on glycoproteins and glycolipids. CLRs represent a large lectin receptor superfamily predominantly expressed by cells of the innate immune system. CLRs recognize conserved glycan structures on pathogens and play a crucial role in the initiation of immune responses.
In our group, the function of CLRs is investigated by using murine models of infection and autoimmunity. We intend to identify novel carbohydrate ligands of CLRs and utilize CLRs for a specific targeting of antigen-presenting cells. Finally, we aim to get a deeper understanding of how CLRs influence inflammatory processes in vivo.
Specifically, we are addressing the following topics (see figure):
- Identification of novel CLR ligands by glycan/glycoprotein array
- Targeting of CLRs using synthetic carbohydrate ligands.
- Investigation of CLR function in murine models of infection and autoimmunity.